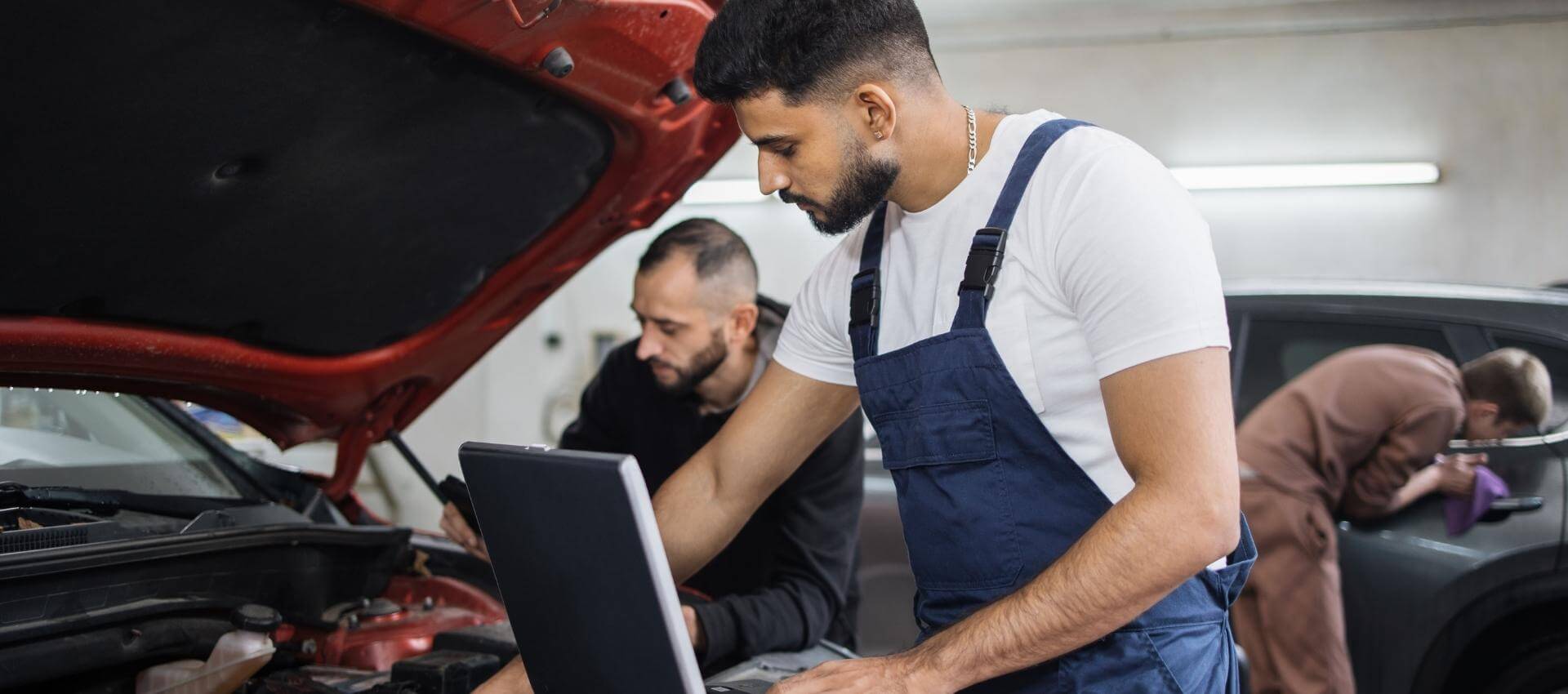
The Ministry of Transport (MOT) test is an essential requirement for all vehicles in the United Kingdom, ensuring that they meet safety and environmental standards. Whether you’re a seasoned driver or a new car owner, understanding the MOT test process is crucial to keeping your vehicle roadworthy and compliant with the law. In this article, we’ll provide a comprehensive guide to help you grasp the ins and outs of the MOT test process.
What is the MOT Test?
The MOT test, mandated by the UK government, stands for the Ministry of Transport test. It’s a mandatory annual examination for vehicles over three years old. The test’s primary purpose is to ensure that vehicles are safe to be on the road and meet environmental standards.
When is the MOT Test Due?
Your vehicle’s first MOT test is due when it’s three years old. After that, it must be tested every year. You can check your vehicle’s MOT due date on your last MOT certificate or by visiting the official UK government website. Remember that driving without a valid MOT certificate is illegal and can result in fines or even the impoundment of your vehicle.
Where to Get an MOT Test?
You can get an MOT test at authorized MOT test centers, which are equipped and certified to perform the examination. Look for a test center displaying the blue sign with three white triangles. They are approved by the Driver and Vehicle Standards Agency (DVSA).

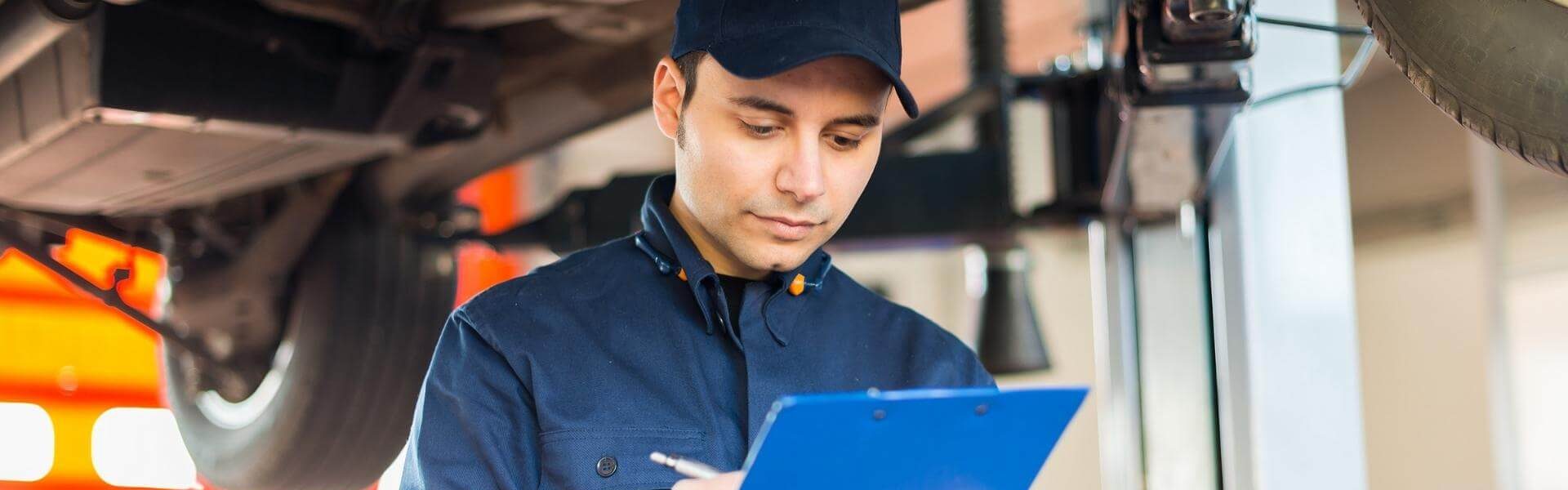
What Does the MOT Test Cover?
The MOT test covers a wide range of safety and environmental checks, including but not limited to:
Vehicle Identification:
This includes checks to ensure the vehicle’s registration plates are in good condition and meet legal requirements.
Lights and Signals:
The condition and alignment of lights, indicators, and reflectors are inspected. Any faulty bulbs should be replaced.
Steering and Suspension:
The steering and suspension components are examined for wear, damage, and proper functionality.
Brakes:
Brake system components, including pads, discs, and the brake fluid, are checked for wear and efficiency.
Tires and Wheels:
Tires are inspected for adequate tread depth and proper inflation. Damaged or excessively worn tires should be replaced.
Seatbelts:
The condition and operation of seatbelts are verified, ensuring they function as designed.
Emissions:
Exhaust emissions are measured to ensure they meet environmental standards, and the exhaust system is checked for leaks.


Body and Structure:
The bodywork and overall vehicle structure are inspected for corrosion and damage.
Wipers and Washers:
Windscreen wipers and washers must be in good working order.
Horn and Mirrors:
The horn and mirrors are checked to ensure they function correctly. What Happens if Your Vehicle Fails the MOT Test?
If your vehicle fails the MOT test, you’ll receive a refusal of an MOT test certificate (VT30). This document details the reasons for failure. You have the option to have the necessary repairs carried out at the test center or at another garage. Once the repairs are completed, you can return for a partial retest, which covers only the failed items.
Understanding the MOT test process is crucial for every vehicle owner in the UK. By staying informed and proactively addressing any issues before your MOT test, you can ensure your vehicle’s safety, compliance with the law, and a hassle-free experience during the examination. Regular maintenance and vigilance will help keep your vehicle roadworthy and protect you, your passengers, and other road users.